原型模式(Prototype Pattern)
wiki:
类型: 创建型
何时使用: 当直接创建对象的代价比较大时,则采用这种模式
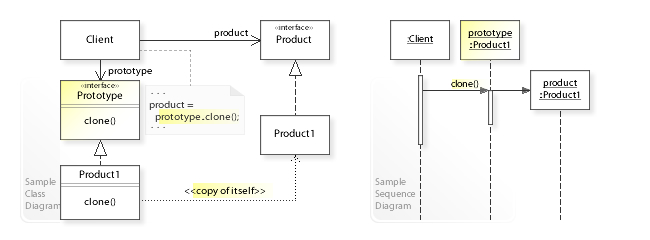
UML
原型设计模式解决了以下问题:
如何创建对象以便在运行时指定要创建的对象?
如何动态加载类的实例化
原型设计模式描述了如何解决这些问题:
定义一个Prototype返回自身副本的对象。
通过复制Prototype对象创建新对象。
原型模式的注意事项:
使用原型模式复制对象不会调用类的构造方法。
单例模式中,只要将构造方法的访问权限设置为private型,就可以实现单例。但是clone方法直接无视构造方法的权限,所以,单例模式与原型模式是冲突的,在使用时要特别注意。
浅拷贝: Object类的clone方法只会拷贝对象中的基本的数据类型,对于数组、容器对象、引用对象等都不会拷贝深拷贝: 将原型模式中的数组、容器对象、引用对象等另行拷贝因为是从内存中直接
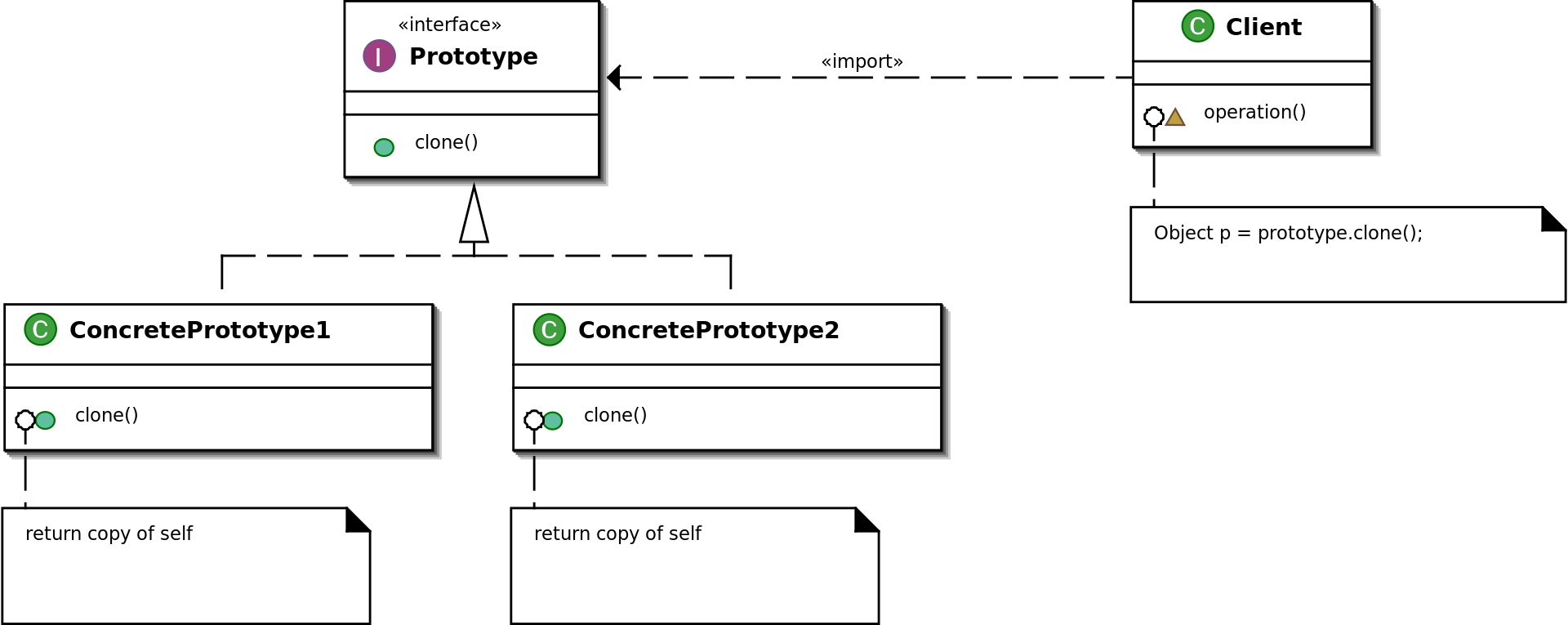
原型模式实例 抽象原型角色
1 2 3 4 5 6 public abstract class Prototype implements Cloneable @Override public Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException return super .clone(); } }
具体原型角色
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class ConcretePrototype1 extends Prototype @Override public Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException return super .clone(); } } public class ConcretePrototype2 extends Prototype private ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); public ConcretePrototype2 () System.out.println("ConcretePrototype2 init..." ); this .list.add("Hello World!" ); } public ArrayList getList () return list; } public void setList (ArrayList list) this .list = list; } @Override public Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException ConcretePrototype2 clone = (ConcretePrototype2)super .clone(); clone.setList((ArrayList) this .getList().clone()); return clone; } }
场景类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public class Client public static void main (String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException ConcretePrototype1 concretePrototype1 = new ConcretePrototype1(); System.out.println(concretePrototype1); System.out.println(concretePrototype1.clone()); System.out.println(); ConcretePrototype2 concretePrototype2 = new ConcretePrototype2(); System.out.println(concretePrototype2); final ConcretePrototype2 clone = (ConcretePrototype2)concretePrototype2.clone(); System.out.println(clone); System.out.println(concretePrototype2.getList()); System.out.println(clone.getList()); System.out.println(); int count = 10000 ; long startTmie = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0 ;i<count;i++){ new ConcretePrototype2(); } long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("new cost :" +(endTime-startTmie)+"ms" ); startTmie = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0 ;i<count;i++){ concretePrototype2.clone(); } endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("prototype cost :" +(endTime-startTmie)+"ms" ); } }
带Prototype Manager的原型模式(登记形式的原型模型)
从缓存(MAP)中获取
可使用HashTable或者ConcurrentHashMap
如果使用HashMap需要考虑加锁,或者Collections.synchronizeMap(hashMap);使其同步
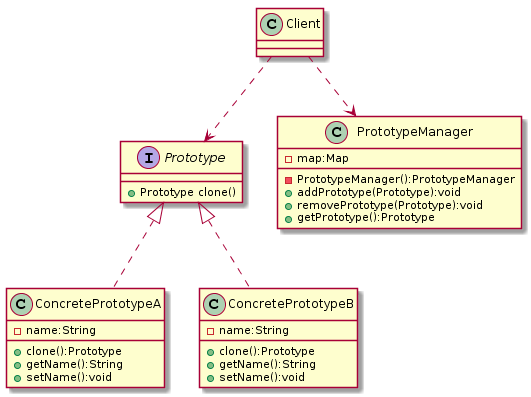
UML
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 @startuml class Client{ } interface Prototype{ + Prototype clone() } class ConcretePrototypeA{ - name:String + clone():Prototype + getName():String + setName():void } class ConcretePrototypeB{ - name:String + clone():Prototype + getName():String + setName():void } class PrototypeManager{ - map:Map - PrototypeManager():PrototypeManager + addPrototype(Prototype):void + removePrototype(Prototype):void + getPrototype():Prototype } Client ..> Prototype Client ..> PrototypeManager Prototype <|.. ConcretePrototypeA Prototype <|.. ConcretePrototypeB @enduml
抽象原型接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public interface Prototype Prototype clone () ; String id () ; }
具体原型对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 public class ConcretePrototypeA implements Prototype private String name; public ConcretePrototypeA (String name) this .name = name; } public String getName () return name; } public void setName (String name) this .name = name; } @Override public Prototype clone () return new ConcretePrototypeA(this .getName()); } @Override public String id () return this .name; } } public class ConcretePrototypeB implements Prototype private String name; public ConcretePrototypeB (String name) this .name = name; } public String getName () return name; } public void setName (String name) this .name = name; } @Override public Prototype clone () return new ConcretePrototypeB(this .getName()); } @Override public String id () return this .name; } }
PrototypeManager
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public class PrototypeManager private static Map<String,Prototype> map = new ConcurrentHashMap(); private PrototypeManager () public static void addPrototype (Prototype prototype) map.put(prototype.id(), prototype); } public static void removePrototype (Prototype prototype) map.remove(prototype.id()); } public static Prototype getPrototype (String id) return map.get(id); } public static Prototype getPrototypeClone (String id) return map.get(id).clone(); } }
场景类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class Client public static void main (String[] args) Prototype prototypeA = new ConcretePrototypeA("ConcretePrototypeA" ); Prototype prototypeB = new ConcretePrototypeB("ConcretePrototypeB" ); PrototypeManager.addPrototype(prototypeA); PrototypeManager.addPrototype(prototypeB); System.out.println(prototypeA); System.out.println(PrototypeManager.getPrototype("ConcretePrototypeA" )); System.out.println(PrototypeManager.getPrototypeClone("ConcretePrototypeA" )); } }
原型模式的优缺点 优点:
性能提高(直接操作内存中的二进制流)
逃避构造函数的约束
缺点:
必须实现 Cloneable 接口
需要为每一个类配置一个克隆方法,而且该克隆方法位于类的内部,当对已有类进行改造的时候,需要修改代码,违反了开闭原则。
在实现深克隆时需要编写较为复杂的代码,而且当对象之间存在多重签到引用时,为了实现深克隆,每一层对象对应的类都必须支持深克隆,实现起来会比较麻烦。