【Design Patterns】装饰器模式
装饰器模式(Decorator Pattern)
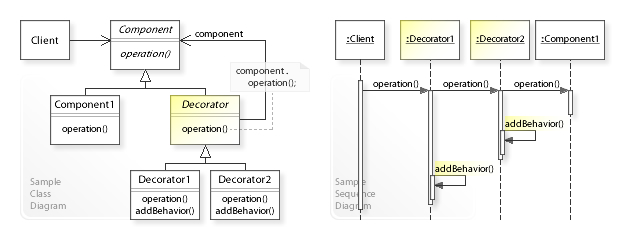
定义: 在面向对象的编程中,装饰器模式是一种设计模式,又名包装(Wrapper),它允许动态地将行为添加到单个对象,而不会影响来自同一类的其他对象的行为。
Definition: In object-oriented programming, the decorator pattern is a design pattern that allows behavior to be added to an individual object, dynamically, without affecting the behavior of other objects from the same class.
类型: 结构型
类比: 装饰者模式在结构上几乎与责任链模式相同,不同之处在于,在一个责任链中,其中一个类正好处理请求,而对于装饰器,所有类都处理请求。
UML
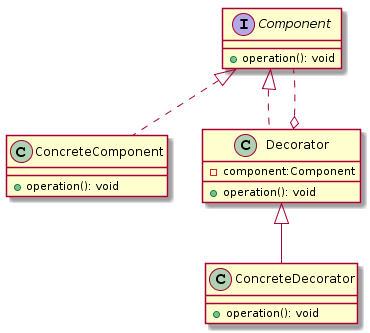
Decorator设计模式可以解决哪些问题?
- 应在运行时动态地将责任添加到对象中(并从中删除)。
- 应提供用于扩展功能(继承)的子类化的灵活替代方案。
Decorator设计模式描述了什么解决方案?
定义那些Decorator对象
Component通过将所有请求转发给它来透明地实现扩展(装饰)对象的接口- 在转发请求之前/之后执行其他功能。
在装饰器模式中的角色有:
- 抽象构件(Component)角色: 给出一个抽象接口,已规范准备接收附加责任的对象。
- 具体构件(ConcreteComponent)角色: 定义一个将要接收附加责任的类
- 装饰(Decorator)角色: 持有一个构件(Component)对象的实例,并定义一个与抽象构件接口一致的接口。
- 具体装饰(ConcreteDecorator)角色: 负责给构件对象“贴上”附加的责任
| Pattern | Intent |
|---|---|
| Adapter or Wrapper | Converts one interface to another so that it matches what the client is expecting |
| Decorator | Dynamically adds responsibility to the interface by wrapping the original code |
| Delegation(委派模式) | Support “composition over inheritance” |
| Facade | Provides a simplified interface |
装饰器实例
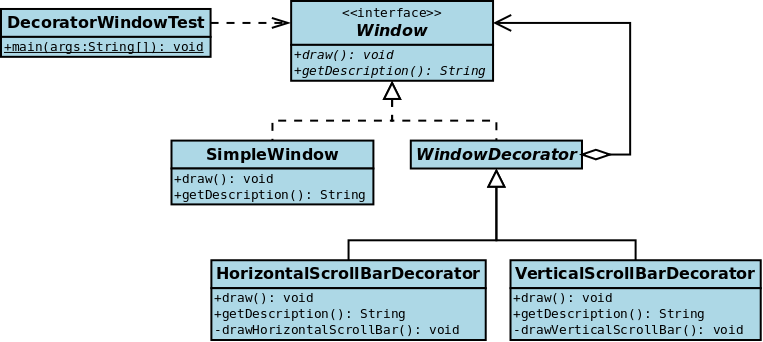
抽象构件(Component)角色:
1 | public interface Window { |
具体构件(ConcreteComponent)角色:
1 | public class SimpleWindow implements Window{ |
装饰(Decorator)角色:
1 | public abstract class WindowDecorator implements Window{ |
具体装饰(ConcreteDecorator)角色:
1 | public class HorizontalScrollBarDecorator extends WindowDecorator{ |
客户端:
1 | public class DecoratedWindowTest { |
装饰器模式的优缺点
优点
- 装饰器模式与继承关系的目的都是要扩展对象的功能,但是装饰器模式可以提供比继承更多的灵活性。装饰器模式允许系统动态决定贴上一个需要的装饰,或者除掉一个不需要的装饰。继承关系是不同,继承关系是静态的,它在系统运行前就决定了
- 通过使用不同的具体装饰器以及这些装饰类的排列组合,设计师可以创造出很多不同的行为组合
缺点
由于使用装饰器模式,可以比使用继承关系需要较少数目的类。使用较少的类,当然使设计比较易于进行。但是另一方面,由于使用装饰器模式会产生比使用继承关系更多的对象,更多的对象会使得查错变得困难,特别是这些对象看上去都很像。
装饰器模式和适配器模式的区别
其实适配器模式也是一种包装(Wrapper)模式,它们看似都是起到包装一个类或对象的作用,但是它们使用的目的非常不一样:
- 适配器模式的意义是要将一个接口转变成另外一个接口,它的目的是通过改变接口来达到重复使用的目的
- 装饰器模式不要改变被装饰对象的接口,而是恰恰要保持原有的接口,但是增强原有接口的功能,或者改变元有对象的处理方法而提升性能